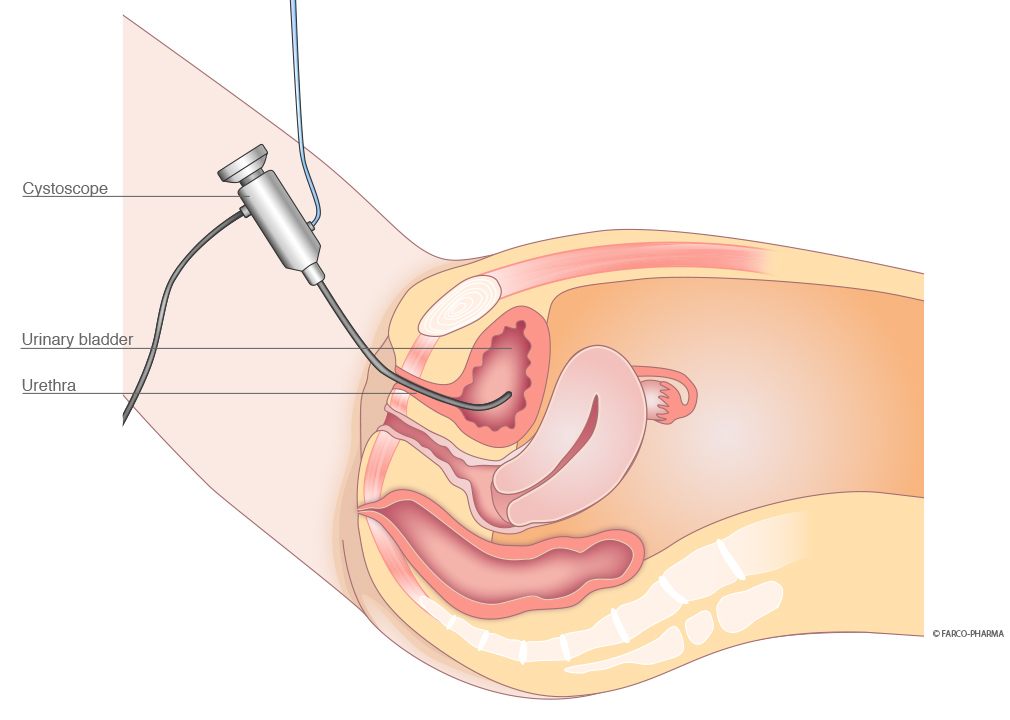
Cystoscopy
An endoscopic examination of the urinary bladder
Cystoscopy (from the Greek: zyst = bladder, skopein = view) is an endoscopic examination, during which the physician examines the urinary bladder with a special endoscope (cystoscope). In men, the prostatic fossa is examined in addition to the urinary bladder and the urethra (cystoscopy). Despite all of the advancements in imaging techniques, e.g. ultrasound and radiography, it is still necessary to perform a cystoscopy in the case of certain conditions.
Cystoscopic technique
A flexible or rigid cystoscope may be used for cystoscopy. A flexible cystoscope adapts more readily to the curved urethra in men and is easier to insert. Conversely, a rigid cystoscope provides better image quality with its lens system and larger irrigation and accessory channels for procedures, such as biopsies. Placement of a camera on the cystoscope enables the image to be viewed on a video monitor.
Reasons for a cystoscopy
Numerous urinary tract conditions may require a cystoscopy in order to confirm a diagnosis. Such conditions include blood in the urine, recurrent inflammations of the urinary bladder, bladder tumours, micturition disorders and urinary stones. In some cases, treatment may also be performed during cystoscopy.
Sequence of the examination
Cystoscopy may be performed as an outpatient intervention. The actual intervention usually lasts from a few minutes to a maximum of 15 minutes. General anaesthetic is only required in children. In adults, a sterile lubricant with local anaesthetic and disinfecting properties, such as Instillagel®, is instilled into the urethra prior to the examination. Once the anaesthetic has taken effect after 5 - 10 minutes, the physician begins the examination.
Potential complications
Cystoscopy may result in subsequent temporary to frequent urinary urgency, urethral burning and small amounts of blood in the urine. Please, consult your urologist in the case of more severe or prolonged symptoms. This risk of injury to the urethra or bladder during cystoscopy is very low. Because cystoscopies are performed under sterile conditions, inflammations of the urinary tract only occur very rarely.